👀 문제
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42588
👊 첫 번째 도전
1. 설계
- Stack에 탑의 위치, 높이를 함께 저장하기위해 Top클래스를 선언한 후, Stack에 푸쉬한다.
- 현재 탑을 now, 왼쪽 값을 next에 저장한다.
- now의 높이가 next 높이보다 크면(now.height>next.height) answer에 next의 위치를 저장한다.
- 아니라면 next는 한 칸 왼쪽 값을 같는다.
- 마지막까지 찾지 못하면 answer=0한다.
- 이때 패스하는 값들은 stTemp에 다시 써야하기 때문에 stTemp에 저장한다.
- answer에 값이 채워지고 stTemp에 값이 존재할 경우 다시 원상복구한다.
2. 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
import java.util.Stack;
/**
*
* @author HEESOO
*
*/
class Top{
int location;
int height;
public Top(int l, int h){
this.location=l;
this.height=h;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] heights) {
int[] answer = {};
Stack<Top> st=new Stack<Top>();
Stack<Top> stTemp=new Stack<Top>();
Top now, next;
for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){
st.push(new Top(i+1,heights[i]));
}
answer=new int[heights.length];
for(int i=heights.length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(st.isEmpty()||st.size()<2){
answer[i]=0;
continue;
}
else{
now=st.pop();
next=st.pop();
}
while(now.height>=next.height){//next조건에 안맞음
if(!st.isEmpty()){
stTemp.push(next);
next=st.pop();
}
else{//next가 없다면
next=null;
break;
}
}//알맞은 next찾음
if(next!=null){
answer[i]=next.location;
st.push(next);
}
else{
answer[i]=0;
}
while(!stTemp.isEmpty()){//stTemp에 값이 있다면 원상복구
st.push(stTemp.pop());
}
}
for(int i=0;i<answer.length;i++){
System.out.println(answer[i]);
}
return answer;
}
}
3. 결과
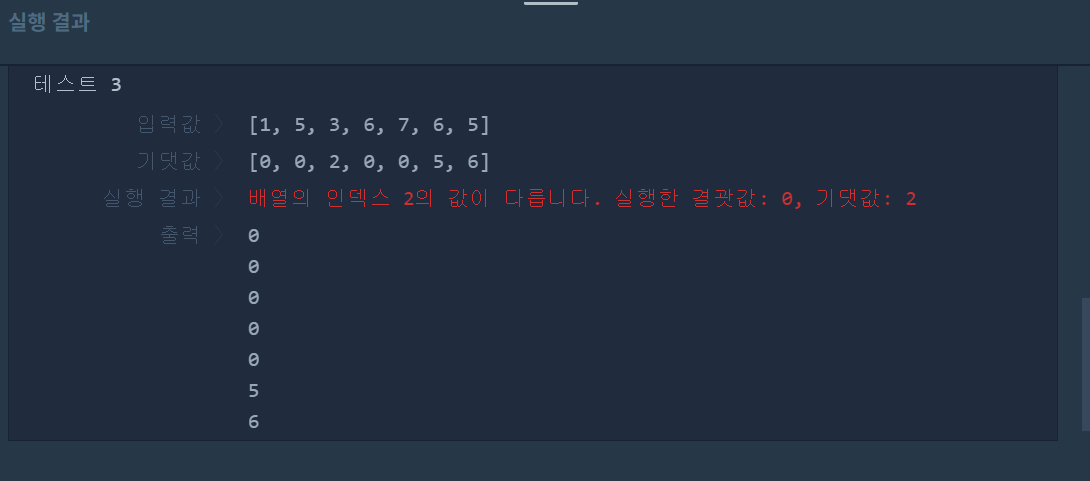
4. 문제점
next의 조건에 안맞아 왼쪽으로 한 칸 이동하였는데, 이때 조건에 맞지않은 next의 값을 따로 저장해두지 않아 방문해야 할 3번째 탑이 사라졌다. 라인19: next 조건에 맞지 않으므로 왼쪽에 조건에 맞는 값이 있는지 확인해야한다. 이때 현재 next의 값이 사라지지 않도록 스택이 비어있는지 유무에 상관없이 stTemp에 저장해둬야한다.
👊 두 번째 도전
1. 설계
- next조건에 맞지 않는 값이 사라지지않도록 stTemp에 저장한다. 이때 스택 st에 원소가 존재하는지 유무와는 관계없다.
2. 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
import java.util.Stack;
/**
*
* @author HEESOO
*
*/
class Top{
int location;
int height;
public Top(int l, int h){
this.location=l;
this.height=h;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] heights) {
int[] answer = {};
Stack<Top> st=new Stack<Top>();
Stack<Top> stTemp=new Stack<Top>();
Top now, next;
for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){
st.push(new Top(i+1,heights[i]));
}
answer=new int[heights.length];
for(int i=heights.length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(st.isEmpty()||st.size()<2){
answer[i]=0;
continue;
}
else{
now=st.pop();
next=st.pop();
}
while(now.height>=next.height){//next조건에 안맞음
stTemp.push(next);
if(!st.isEmpty()){
next=st.pop();
}
else{//next가 없다면
next=null;
break;
}
}//알맞은 next찾음
if(next!=null){
answer[i]=next.location;
st.push(next);
}
else{
answer[i]=0;
}
while(!stTemp.isEmpty()){//stTemp에 값이 있다면 원상복귀
st.push(stTemp.pop());
}
}
for(int i=0;i<answer.length;i++){
System.out.println(answer[i]);
}
return answer;
}
}
- Document nowDoc: ArrayList의 첫 번째 값(또는 그 다음 값)을 나타낸다. 앞에 최댓값이 있을 경우 다음으로 넘어간다.
- Document nextDoc: nowDoc 뒤의 값들이다.
- ArrayList
array: 중요도와 순서의 값을 가지는 Document클래스를 생성하여 ArrayList에 저장한다. 중간에서 값을 삭제하고 맨 뒤에 추가할 경우가 있으므로 이가 쉬운 ArrayList를 사용한다.
3. 결과
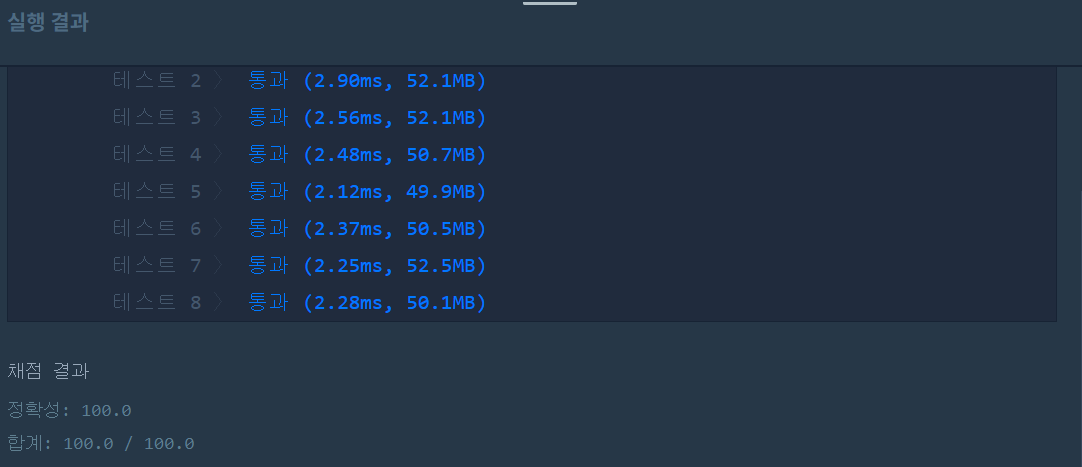
👏 해결 완료!
스택으로 풀다가 잘 안되서 링크드리스트를 생각했는데, next의 값을 바꿔버리면 다음 노드를 방문할 수 없으므로 포기했다. 다음으로 더블링크드리스트로 next로 탑을 순서대로 하고 prev로 송신할 수 있는 탑을 가리키도록 하는 건 어떨까 생각해봤지만, 라이브러리에 있는 구조를 이용하면서 prev와 next를 어떻게 바꾸는지 모르겠어서 포기했다(그렇다고 더블을 구현하는건 아닌 것 같아서^0^).